Expression Functions in Query Manager
An EXPRESSION utilizes special query functions to manipulate the appearance of data in your output or criteria. Expressions can
be used one of two ways: to display a calculated field, or to restrict the output via a more complex criterion.
Procedure
1.
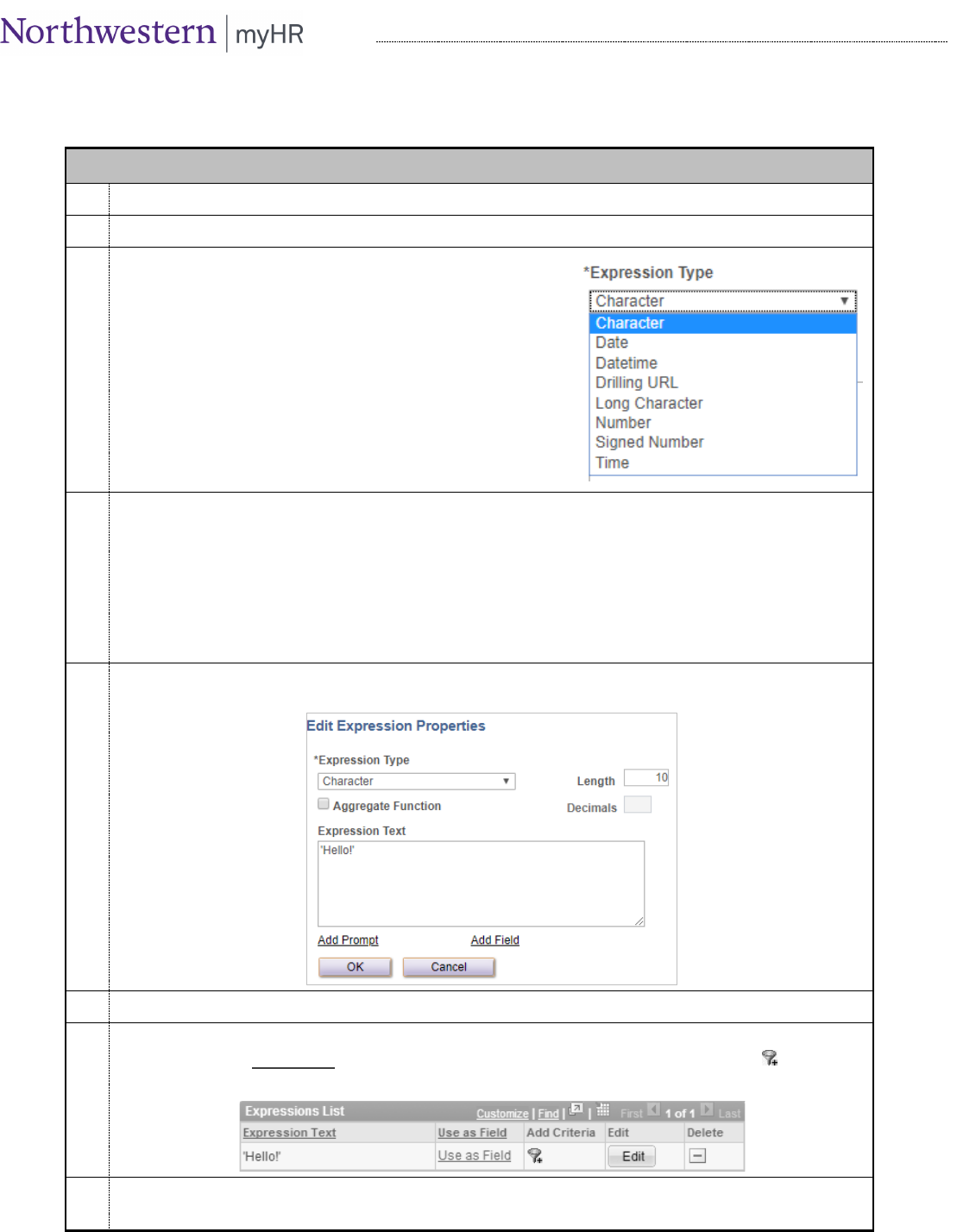
Click the Expressions tab.
2.
Click the Add Expression button.
3.
In the Expression Type box, choose the type of data that your
expression will create. The most common data types used will
be:
• “Character” – if your data will be letters, numbers, or a
combination of both.
• “Date” – if your data will create a full date (including
month, day, and year).
• “Number” – if your data will create a number or decimal
that will be operated on in the query (such as adding,
summing or averaging).
4.
Enter the Length and Decimal values if required:
• If using a “Character” type, Length is the maximum number of characters in the data. Decimals is not
required.
• If using a “Date” type, neither is required.
• If using a “Number” type, Length is the total number of digits, including decimal places; Decimals is
the number of decimal places. (Ex: a dollar amount of 15345.00 would have a Length of 7 and a
Decimal of 2.)
5.
Enter the Expression Text. (See the following pages for specific expression text.) For example:
6.
Click OK.
7.
At this point, your expression is part of the query like any other field. You can add it as a column to your
results by choosing Use as Field, or you can add a criteria on it by clicking the criteria funnel :
8.
Tips: Character constants have to be delimited by single quotes (e.g. 'FAC'); don’t use double quotes in your
expressions. In the function descriptions below, brackets [ ] mean optional values.

Expression Functions PAGE 2
Northwestern University HR Operations, Reporting, and Analytics
IF-THEN-ELSE FUNCTION
DECODE
DECODE can be used as a simple “If-Then-Else” statement to test one field against one or more values.
SYNTAX
DECODE( expression , searchfor , result [, searchfor , result]... [, default] )
PARAMETERS
expression - the expression or field that you are testing
searchfor – the value that is compared against the expression
result – the value that is returned/displayed if expression = searchfor
default – (optional) the value that is returned when expression does not match any searchfor
EXAMPLE
DECODE(A.POSN_TYPE, 'FAC', 'Faculty', 'STF', 'Staff', 'STU', 'Grad Student', 'Temp')
CASE
CASE may be used for a more intricate If-Then-Else test, where multiple expressions, fields, or combinations of fields need to be
tested at the same time – or when the fields need to be tested against other expressions or fields.
SYNTAX
CASE [expression]
WHEN condition THEN result
[WHEN condition THEN result]...
[ELSE default]
END
PARAMETERS
expression – (optional) the field or expression to test, only if all WHEN statements are testing the same expression. This is
similar to using the
DECODE function.
condition – the value or full expression/field to test. Each condition must be the same datatype. Conditions must be
listed in order of importance; once one
condition is satisfied, its result is returned and no other condition will be tested.
result – the value that is returned/displayed if condition is satisfied.
default – (optional) the value that is returned when none of the conditions is satisfied.
EXAMPLES
CASE
A.POSN_TYPE
WHEN 'FAC' THEN 'Faculty'
WHEN 'STF' THEN 'Staff'
WHEN 'STU' THEN 'Grad Student'
ELSE 'Temp'
END
CASE
WHEN A.POSN_CATEGORY = 'RES' THEN 'Research Faculty'
WHEN A.POSN_TYPE = 'FAC' THEN 'Non-Research Faculty'
WHEN A.POSN_TYPE = 'STF' THEN 'Staff'
WHEN A.PAYGROUP = 'MGW' OR A.JOBCODE = '100029' OR
A.JOBTITLE LIKE '%WS' THEN 'Student'
WHEN A.JOBTITLE LIKE '%(SP)' THEN 'Special Pay'
WHEN A.PAYGROUP = 'BIT' THEN 'Temp'
ELSE A.JOBTITLE
END
Expression Functions PAGE 3
Northwestern University HR Operations Reporting & Analytics
DATE/TIME FUNCTIONS
SYSDATE (current date/time)
SYSDATE returns the current day and time.
SYNTAX
SYSDATE
PARAMETERS
There are no additional parameters for this function.
EXAMPLES
CAST(SYSDATE AS TIMESTAMP) returns current day and time
TRUNC(SYSDATE) returns the current day only, without the time
TRUNC(SYSDATE)+7 returns the date for one week from the current day, without the time
Add or Subtract Days
To add or subtract days from a date field, use the traditional (+) and (-) operators.
SYNTAX
date + days or
date - days
PARAMETERS
date – any field of date format.
days – the number of days to add or subtract.
EXAMPLES
A.EFFDT + 7 returns seven days after the effective date
A.EFFDT - 7 returns seven days prior to the effective date
NOTE
• When using a datetime field, remember the impact of time. For example, 10/10/2015 12:00pm + 7 will yield 10/17/2015
12:00pm. To remove the time portion of a datetime field, use
TRUNC.
ADD_MONTHS
ADD_MONTHS returns a date at the specified number of months in the past or future.
SYNTAX
ADD_MONTHS(date, months)
PARAMETERS
date – any field of date format.
Expression Functions PAGE 4
Northwestern University HR Operations, Reporting, and Analytics
months – the number of months to add (positive number) or subtract (negative number).
EXAMPLES
ADD_MONTHS(A.EFFDT, 1) returns one month from the effective date
ADD_MONTHS(A.EFFDT, -1) returns one month prior to the effective date
NOTES
• If the calculation returns a date that doesn’t exist, it will be rounded to the last day of that month. For example, adding one
month to 1/30/15 will return 2/28/15.
• When using a datetime field, remember the impact of time. To remove the time portion of a datetime field, use
TRUNC.
TRUNC (truncate date/time field)
TRUNC can be used to truncate a date or datetime field to a specific unit of measure.
SYNTAX
TRUNC(field [, 'format'])
PARAMETERS
field - a field or expression of date or datetime format that you wish to truncate.
format – (optional) indicates how the field should be truncated according to the following options in the following table.
EXAMPLES
To truncate to…
Use format…
Example
11/28/2015 12:05:03.2314
becomes…
Day (remove the time)
(none)
TRUNC(A.LASTUPDDTTM)
11/28/2015
Month
MONTH
TRUNC(A.LASTUPDDTTM, 'MONTH')
11/01/2015
Year
YEAR
TRUNC(A.LASTUPDDTTM, 'YEAR')
01/01/2015
Hour
HH
TRUNC(A.LASTUPDDTTM, 'HH')
11/28/2015 12:00
Minute
MI
TRUNC(A.LASTUPDDTTM, 'MI')
11/28/2015 12:05
Reformatting Date Fields
Using expressions, you can easily reformat a date field to display differently. Because PeopleSoft stores different date fields in
different ways, you may need to translate the date into a different data type first.
SYNTAX
• If the date field is stored in PeopleSoft as a “date” type, such as an Effective Date:
TO_CHAR(TO_DATE(field), 'format')
•
If the date field is stored in PeopleSoft as a “time” type, such as Course Session Start Time:
TO_CHAR(TO_TIMESTAMP(field, 'HH24.MI.SS.FF'), 'format')
• If the date field is stored as plain text, such as Last Updated Date/Time, you must specify its existing format before re-
formatting it:
TO_CHAR(TO_DATE(field, 'currentformat'), 'format')

Expression Functions PAGE 5
Northwestern University HR Operations Reporting & Analytics
PARAMETERS
The format must be in single quotes and specifies the formatting you’d like to apply to the date:
Date Code Meaning Date Code Meaning
YYYY
4-digit year
DY
Abbreviated name of day.
YY
2-digit year
HH
Hour of day (1-12)
MM
Month (01-12; JAN = 01)
HH24
Hour of day (0-23)
MON
Abbreviated name of month
MI
Minute (0-59)
DAY
Name of day
SS
Second (0-59)
DD
Day of month (1-31)
AM
Meridian indicator
EXAMPLES
For an Effective Date of 2015-01-06:
TO_CHAR(TO_DATE(A.EFFDT), 'YYYY') -> 2013
TO_CHAR(TO_DATE(A.EFFDT), 'MON DD, YYYY') -> Jan 6, 2013
TO_CHAR(TO_DATE(A.EFFDT), 'MM/DD/YYYY') -> 01/06/2013
STRING FUNCTIONS
|| (concatenate)
|| (two vertical bars) may be used to concatenate any number of strings, fields, and expressions together.
SYNTAX
expression || expression [|| expression]...]
PARAMETERS
expression – a field, string (in single quotes), or expression. Multiple pieces may be concatenated together by using the
vertical bars multiple times
EXAMPLE
A.NW_POSN_TYPE || '/' || A.NW_POSN_CATEGORY returns a value like FAC/REG
REPLACE
REPLACE searches for specific text within a field and replaces it with something else.
SYNTAX
REPLACE(expression, searchfor [, replacewith])
PARAMETERS
expression - the field or expression that you are looking to replace within
searchfor – the value you are looking for
replacewith – (optional) if searchfor is found, it will be replaced with replacewith
EXAMPLE
REPLACE(A.NW_EMAIL_ADDRESS, 'northwestern.edu', 'n...') returns a value like j-smith@n...

Expression Functions PAGE 6
Northwestern University HR Operations, Reporting, and Analytics
SUBSTR (substring)
SUBSTR finds and extracts only a specific part of the data field or expression text.
SYNTAX
SUBSTR(expression, startposition [, length])
PARAMETERS
expression - the field or expression that you are looking to extract a piece from.
startposition – the position of the character you want to start at, beginning with 1. A positive number n will begin at the
nth character from the left; a negative number -n will begin at the nth character from the right.
length – (optional) the number of characters to return. If not provided, the rest of the characters to the end of the string will
be included.
EXAMPLE
SUBSTR(A.DEPTID, 1, 4) returns the first four digits of the department number
Constants
A constant may be added as an expression by simply enclosing the text in single quotes.
SYNTAX
'constant'
PARAMETERS
constant – the text that you want to display. Note that you cannot use quotation marks directly. To include a single or
double quote, use
CHR(34) or CHR(39) respectively, utilizing the || function.
EXAMPLES
'Employee' returns Employee for each row of data
CHR(39) || 'Employee' || CHR(39) returns “Employee” for each row of data
NOTE
• As illustrated above, the || (concatenate) function can be combined with strings, field names, and other expressions to join
different pieces of data into one expression.
Other String Functions
Expression Description
INITCAP(field)
Capitalizes the first letter of each word.
LOWER(field)
Converts the entire field to lowercase.
UPPER(field)
Converts the entire field to uppercase.
Expression Functions PAGE 7
Northwestern University HR Operations Reporting & Analytics
LTRIM(field [, totrim])
RTRIM(field [, totrim])
TRIM(field [, totrim])
Removes characters from the left, right, or both sides of a
field respectively. If totrim is omitted, leading or trailing
spaces will be removed. Otherwise, will remove the
totrim
character that occurs at the beginning or end of string.
%OPERATORID
The myHR UserID or NetID of the current user.
NUMERICAL & MATHEMATICAL FUNCTIONS
Rounding Functions
Expression Description
CEIL(field)
Rounds up to the nearest integer.
FLOOR(field)
Rounds down to the nearest integer.
ROUND(field [, decimal_places])
Rounds the field to the indicated number of decimal places. If
decimal_places is omitted, it rounds to the nearest whole
number.
Comparative Functions
Expression Description
GREATEST(field1, field2, ...)
Returns whichever field in the list has the greatest value.
LEAST(field1, field2, ...)
Returns whichever field in the list has the least value.
Mathematical Functions
Expression Description
ABS(field)
Returns the absolute value.
MOD(field1, field2) or
REMAINDER(field1, field2)
Returns the remainder of
field1
divided by
field2.
Aggregate Functions
Although aggregate functions can be selected on the Fields tab in Query Manager, creating an expression for an aggregate
function allows your query to retain access to the regular field value. This is useful if you need to use that field value as a
Criteria, or if you wish to include both the value and the aggregate in a single query.
Expression Description
AVG(field)
MAX(field)
MIN(field)
MEDIAN(field)
SUM(field)
The average, maximum, minimum, or median of all values for that
field, where everything else in a row is the same.

Expression Functions PAGE 8
Northwestern University HR Operations, Reporting, and Analytics
COUNT([DISTINCT] field)
The count of all values for that field, where everything else in a row is
the same. Including DISTINCT will count only the distinct values that
appear (duplicates will not be counted).
OTHER FUNCTIONS
LISTAGG
LISTAGG combines values from multiple result rows into one cell, where everything else in the row is the same. This is an
aggregate function.
SYNTAX
LISTAGG(field, [, 'delimiter']) WITHIN GROUP (ORDER BY field)
PARAMETERS
field - the field for which values will be combined, when all other data in the row is the same.
delimiter – (optional) the delimiter used to separate values that are combined.
EXAMPLE
LISTAGG(A.JOBTITLE, ', ') WITHIN GROUP (ORDER BY A.JOBTITLE) for someone who has multiple
jobs, it will return things like: Professor, Director of Research Center, A. B. Smith Professor
NVL (null substitution)
NVL allows you to substitute a specific value when the field or expression you are looking for is null.
SYNTAX
NVL(expression, 'default')
PARAMETERS
expression - the field or expression; this will be returned if it exists.
default – the string that will be returned when expression is null.
EXAMPLE
NVL(A.NW_GL_AMT, '0.00')
